¶ 1. Overview of GitLab Pages
¶ ❓ What Is GitLab Pages?
GitLab Pages is the built‑in static website hosting feature of GitLab (available on GitLab.com and Self‑Managed). It enables auto‑deployment of static sites—generated by Hugo, Jekyll, MkDocs, or plain HTML/CSS/JS—directly from Git as part of the CI/CD workflow. You can use either GitLab’s default *.gitlab.io domain or a custom Pages domain, and support HTTPS and visibility control.
¶ 🚀 Key Features
- CI/CD–native deployments: Defines
pages: truein.gitlab-ci.ymlto build and publish static artifacts. - SSG support: Works with Hugo, Jekyll, Hexo, MkDocs, Gatsby, or raw static files.
- Custom domains & TLS: Supports Let’s Encrypt auto‑certification or custom wildcard certificates.
- Access control: Restrict site visibility to authenticated GitLab users; requires instance‑level
pages.access_control. - Horizontal scaling: Compatible with object storage (S3, MinIO) and Pages-only nodes for multi‑node deployments.
- Multi‑version/branch previews:
path_prefixintroduced from GitLab 16.7 (GA in 17.9) enables per-branch preview environments.
¶ 🏗 Access Gitlab Pages Workfolw Overview
Self‑hosted setups may co-locate Pages daemon or use dedicated nodes with shared storage.
¶ 2. 🧪 Lab: Activating GitLab Pages on Self‑Hosted GitLab
The instructions below assume Omnibus Linux installation, sudo or root access, and a prepared domain (e.g. gitlab-pages.wildsre.com) not subdomain to your GitLab instance (gitlab.wildsre.com).
¶ 2.1 Domain & DNS Preparation
- Choose a Pages domain that for GitLab Pages URL (e.g.
gitlab-pages.wildsre.comis this hands-on lab). - Wildcard mode (
namespace.example.io):
*.gitlab-pages.wildsre.com. A 192.168.0.12 # For gitlab_pages['namespace_in_path'] = false
gitlab-pages.wildsre.com. A 192.168.0.12 # For gitlab_pages['namespace_in_path'] = true
¶ 2.2 Update Gitlab configure
Option 1: For wildcard domain configuration
$ sudo vim /etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb
gitlab_pages['enable'] = true
pages_external_url 'https://gitlab-pages.wildsre.com'
pages_nginx['redirect_http_to_https'] = true
pages_nginx['ssl_certificate'] = "/etc/gitlab/ssl/gitlab-pages.wildsre.com.fullchain.pem"
pages_nginx['ssl_certificate_key'] = "/etc/gitlab/ssl/gitlab-pages.wildsre.key.pem"
gitlab_pages['access_control'] = true # must enable if you intend to restrict access
Option 2: For single-domain mode(provided Gitlab >= 16.11)
$sudo vim /etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb
gitlab_pages['enable'] = true
pages_external_url 'https://gitlab-pages.wildsre.com'
gitlab_pages['namespace_in_path'] = true
pages_nginx['redirect_http_to_https'] = true
pages_nginx['ssl_certificate'] = "/etc/gitlab/ssl/gitlab-pages.wildsre.com.fullchain.pem"
pages_nginx['ssl_certificate_key'] = "/etc/gitlab/ssl/gitlab-pages.wildsre.key.pem"
gitlab_pages['access_control'] = true
Apply changes:
$ sudo gitlab-ctl reconfigure
$ sudo gitlab-ctl restart
After the configure change, you can check the pages feature in repo --> Deploy menu like below.
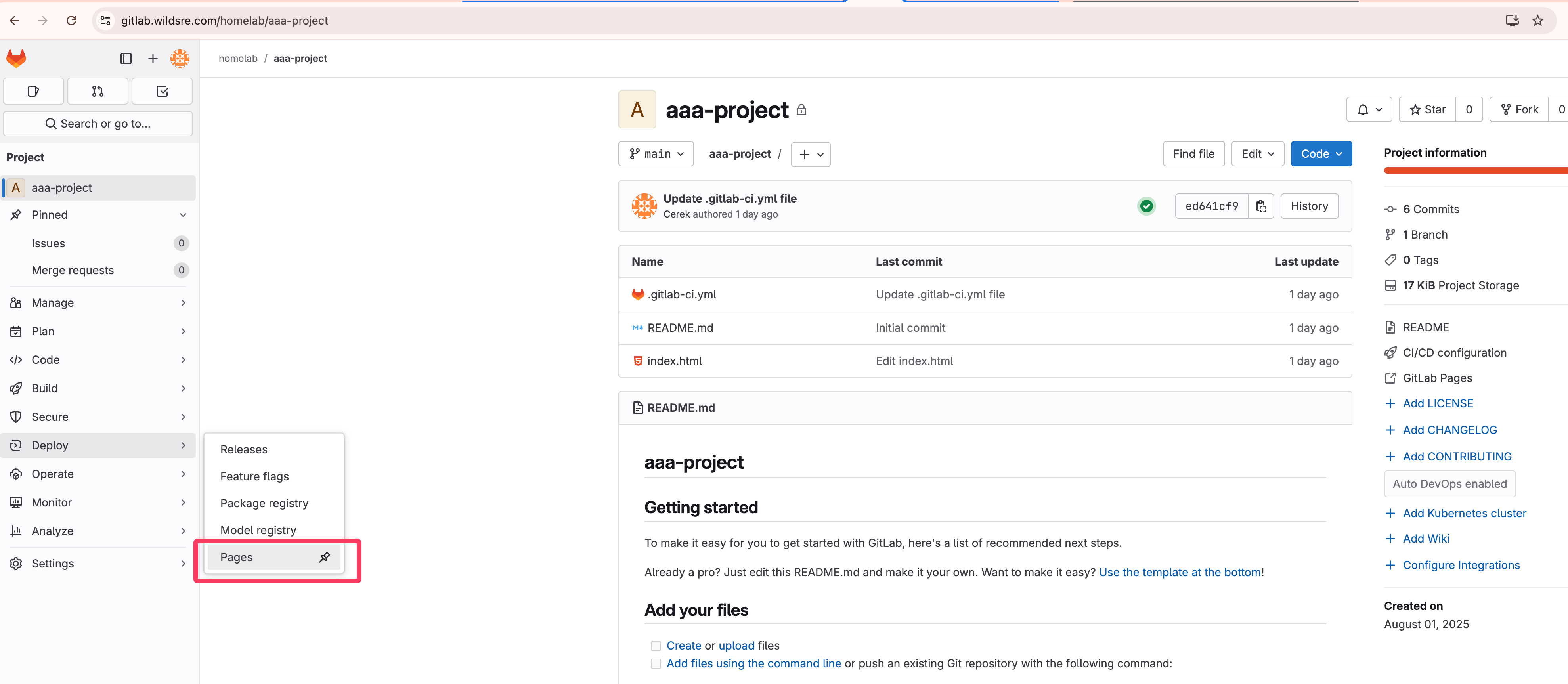
¶ 3. 🧪 Lab: Deploy Pages via Gitlab CI/CD Action
¶ 3.1 First Attempt: A Simple GitLab Pages Deployment
This example demonstrates how to deploy a simple index.html using GitLab Pages with no static site generator involved.
The .gitlab-ci.yml file content like below:
pages:
stage: deploy
script:
- mkdir public
- cp index.html public/
artifacts:
paths:
- public
only:
- main # or "master", depending on your default branch
📝 Notes
- The public/ folder is required by GitLab Pages as the root for deployment.
- This
.gitlab-ci.ymlfile copies index.html into public/, then GitLab will host it automatically. - After pushing to the main branch, the site will be accessible at:
The Gitlab Pipeline status like below:
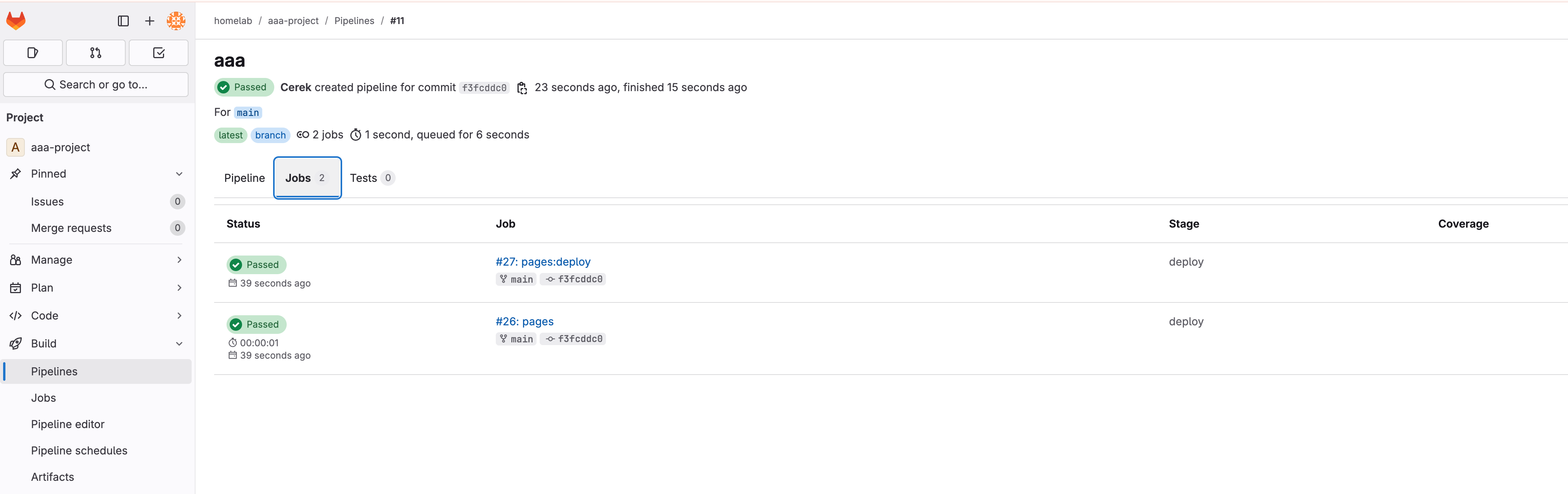
The Gitlab repo pages status like below:

Access the Gitlab Pages:
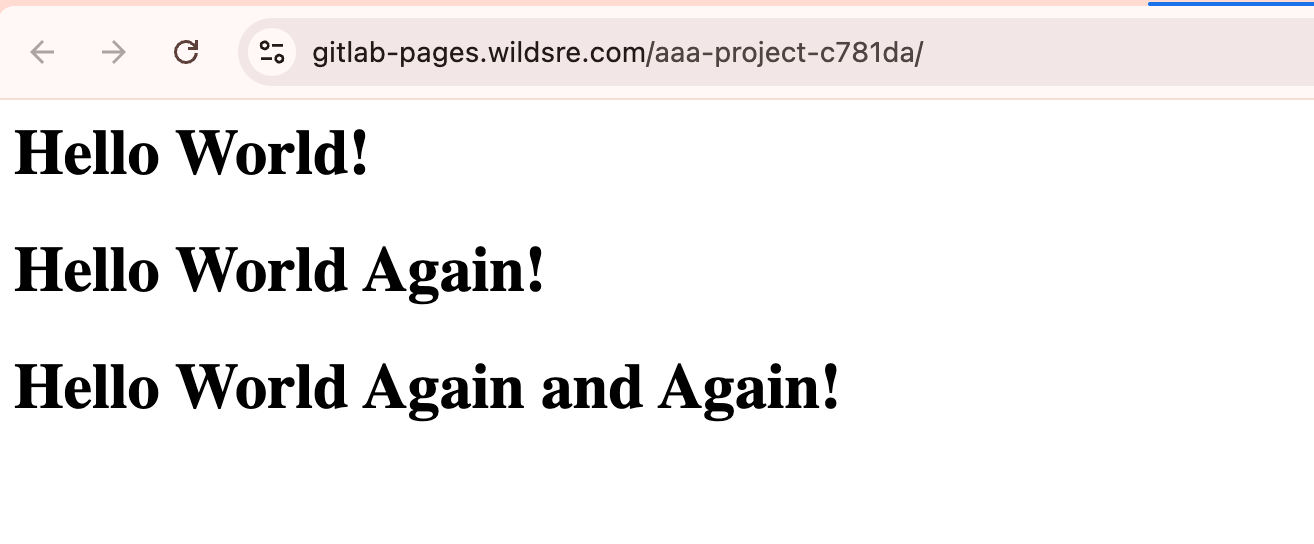
This is the simplest working setup to publish content using GitLab Pages. It's ideal for fast prototyping, documentation, or hosting small static websites.
¶ 3.2 Deploy Hugo Website to Pages
This example demonstrates how to deploy Hugo project to Gitlab Pages.
The .gitlab-ci.yml file content like below:
image: docker.io/hugolicious/hugo:latest
variables:
HUGO_BASE_URL: "https://example.io/${CI_PROJECT_NAMESPACE}/${CI_PROJECT_NAME}"
stages:
- build
- deploy
build_site:
stage: build
script:
- hugo --minify --baseURL="${HUGO_BASE_URL}"
artifacts:
paths:
- public
pages:
stage: deploy
dependencies:
- build_site
script:
- echo "Deploying Hugo artifacts"
pages: true
artifacts:
paths:
- public
expire_in: 1 week
rules:
- if: '$CI_COMMIT_REF_NAME == $CI_DEFAULT_BRANCH'
¶ 4. ✅ Summary & Best Practices
GitLab Pages allows you to publish static websites directly from your repository using GitLab CI/CD. It’s easy to set up and ideal for personal sites, documentation, or project previews.
¶ Key Takeaways
- Fast Setup: Use
.gitlab-ci.ymlto deploy any static content-just place files in thepublic/folder. - Flexible Domains: You can use GitLab’s default domain or set up a custom domain with HTTPS.
- Access Control: Pages can be public or restricted to logged-in GitLab users.
- Scalable: Works with object storage and supports multi-node setups for large teams.
- Branch Previews: Enable
path_prefixto preview pages per branch (available in GitLab 16.7+).
¶ Best Practices
| Topic | Tip |
|---|---|
| CI/CD Setup | Keep .gitlab-ci.yml clean and use rules to control deployments. |
| Domain & HTTPS | Use wildcard DNS for subdomains or enable namespace_in_path mode. |
| Visibility | Set proper project visibility; enable access control if needed. |
| Debugging | Use gitlab-ctl tail to check logs if Pages don't load as expected. |
| TLS Certificates | Let’s Encrypt or custom certs both supported in GitLab Pages. |
GitLab Pages is a powerful way to bring your static content to the web with minimal effort. Start simple—then scale as you grow.